Design for Sustainability (DfS)
Design for Sustainability (DfS) means creating products and processes that are smarter, greener, and built to last. By reducing waste, saving resources, and cutting impacts across the life cycle, DfS helps businesses innovate while staying aligned with sustainability goals and regulations.

Key Principles of DfS
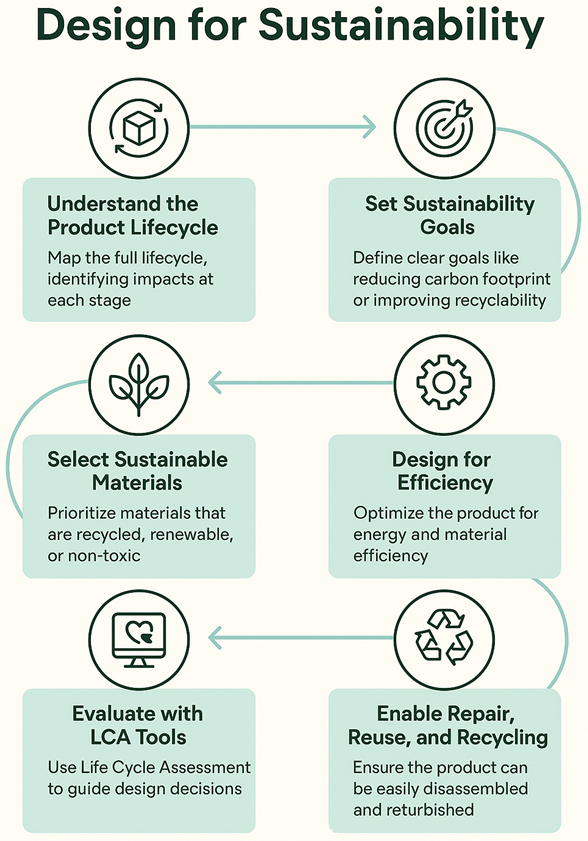
❖ Understand the Product Life Cycle
Map the complete lifecycle of the product, from raw material extraction to disposal, to identify sustainability hotspots and assess environmental, social, and economic impacts at each stage.
❖ Set Clear Sustainability Goals
Define clear goals such as reducing carbon footprint, minimizing resource use, enhancing energy efficiency, or improving product recyclability.
❖ Select Sustainable Materials
Choose materials with low environmental impact, including recycled, renewable, or certified resources. Emphasize durability, safety, and non-toxicity in material selection.
❖ Design for Efficiency
Optimize design to reduce energy and material inputs during manufacturing, transportation, and use. Eliminate unnecessary complexity and minimize production waste in all phases.
❖ Enable Repair, Reuse, and Recycling
Design modular components, easy disassembly, and clear labeling to support repairability, refurbishment, and recycling at the product’s end-of-life.
❖ Evaluate with LCA Tools
Apply LCA tools to quantify environmental impacts, validate sustainability improvements, and guide data-driven design choices.
❖ Engage Stakeholders Across the Value Chain
Collaborate with suppliers, end-users, and recyclers to co-develop sustainable solutions and increase product acceptance, compliance, and circularity.